Proofs Without Peeking: The Magic Behind Zero-Knowledge Proofs
- Henil Diwan

- Jun 13, 2025
- 6 min read
Imagine this: you’ve got a secret—something powerful, valuable, or deeply personal. Now imagine being able to prove you know that secret, without actually revealing a single thing about it. Sounds like a magic trick, right? Welcome to the fascinating world of zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs)—one of the most mind-bending innovations in modern cryptography.
As we delve into the world of zero-knowledge proofs, we’ll explore the foundational principles that power this technology, examine its diverse and growing range of applications, discuss the advantages it offers in terms of privacy and efficiency, and consider how it is shaping the future of secure digital interactions.
What Are Zero-Knowledge Proofs?
At its core, a zero-knowledge proof allows one party to convince another that a given statement is true—without revealing why it’s true or disclosing any additional information. Imagine being able to verify your identity, prove ownership, or demonstrate knowledge of a secret, all without actually sharing the details. It’s a revolutionary concept that blends mathematics and cryptography in truly ingenious ways.
The requirement here is straightforward: one party (the prover) must convince another (the verifier) that a particular statement is true, all while the prover keeps the information private.
To ensure this process is both reliable and secure, ZKPs adhere to three fundamental properties:
Completeness: If the statement is true and both parties follow the protocol correctly, the verifier will be convinced by the prover’s evidence.
Soundness: If the statement is false, no dishonest prover can convince the verifier that it’s true—at least not without an extremely small probability of success.
Zero-Knowledge: Most importantly, if the statement is true, the verifier learns nothing beyond that fact. No additional information is leaked—no data, no secrets, just the assurance that the prover knows what they claim to know.
Think of it like a magic trick: a magician can show an audience they have a rabbit without ever letting anyone see the rabbit itself. It's there, but hidden from view.
This balance between verification and secrecy is what makes ZKPs so powerful in today’s digital landscape. As we increasingly rely on systems that require authentication, data sharing, and verification, the ability to prove something without exposing it becomes not only valuable, but essential.
How Do Zero-Knowledge Proofs Work?
Behind the illusion of ZKPs is a foundation of rigorous mathematics and cryptographic design. ZKPs are built on computational problems that are easy to perform in one direction but nearly impossible to reverse without specific knowledge, a principle that ensures both security and privacy.
The Interactive Protocol: : A Dialogue of Proof
One of the earliest and most intuitive forms of ZKPs is the interactive protocol. In this setup, two parties engage in a structured conversation: the prover, who claims to know a secret, and the verifier, who seeks assurance that the claim is valid without learning the secret itself.
Here’s how it works: the prover initiates the process by asserting that a particular statement is true. The verifier then issues a series of challenges—carefully designed questions meant to test the prover’s knowledge. The prover responds in a way that demonstrates they truly possess the information, without ever disclosing it. If the prover can consistently answer these challenges across multiple rounds, the verifier gains confidence in the claim's validity.
A famous analogy used to explain this is the Ali Baba Cave thought experiment. Imagine a circular cave with a locked door on one path. The prover claims to know the secret word that opens the door. To test this, the verifier waits outside the cave and asks the prover to emerge from a specific path. If the prover can appear from either side on demand—without the verifier ever seeing the actual door open—it proves they know the secret word, even though they’ve never revealed what it is.

The Non-Interactive Protocol: : Proof in a Single Message
While interactive ZKPs are conceptually elegant, they can be inefficient in practice, especially in distributed systems like blockchains where back-and-forth communication is impractical. This is where non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs (NIZKs) come into play.
In a non-interactive protocol, the prover generates a standalone proof that encapsulates all the necessary information. This proof can be verified by anyone, at any time, without requiring a live exchange between parties. It's a powerful advancement that makes zero-knowledge proofs scalable and efficient for real-world applications, particularly in privacy-preserving cryptocurrencies and decentralized identity systems.
Technologies like zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Arguments of Knowledge) and zk-STARKs are leading implementations of this non-interactive approach. They allow systems to validate complex computations or transactions without revealing the data behind them—all in a concise and verifiable format.
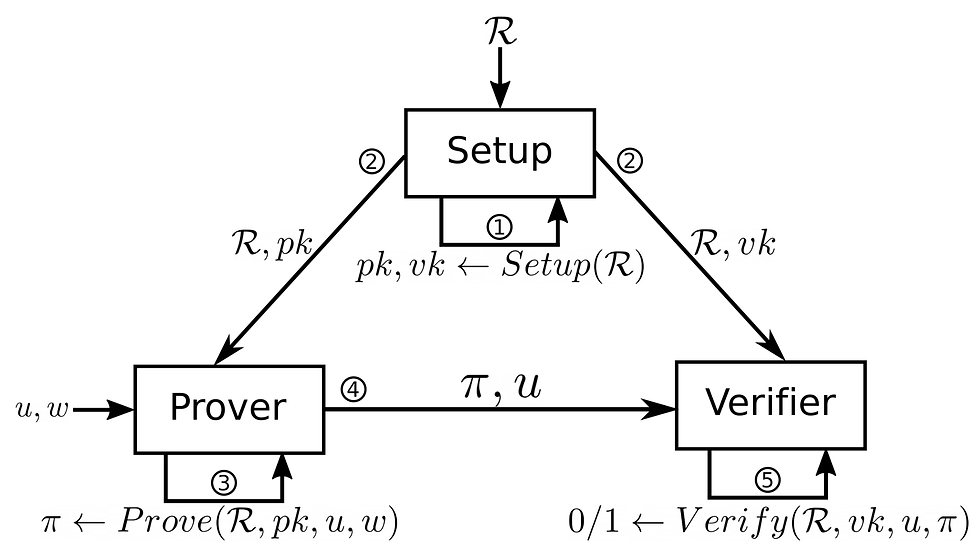
Applications of Zero-Knowledge Proofs
Zero-knowledge proofs are transforming the way we think about privacy, trust, and verification across numerous industries. Their ability to confirm the validity of information without revealing the information itself is driving innovation in digital security, particularly in areas where privacy and integrity are paramount. Below are some of the most impactful applications:
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain Privacy
One of the most prominent and practical uses of ZKPs is in the realm of cryptocurrencies. In traditional blockchain systems, transparency often comes at the cost of privacy. Zero-knowledge proofs offer a solution by enabling fully private transactions.
Take Zcash, for instance—a cryptocurrency that leverages ZKPs, specifically zk-SNARKs, to allow users to send and receive funds without disclosing transaction details such as sender, recipient, or amount. This ensures transaction validity without exposing sensitive financial data, effectively marrying privacy with the immutability and trustlessness of blockchain technology.
Authentication Systems
Zero-knowledge proofs are revolutionizing authentication systems, making it possible for users to prove their identity without revealing passwords or personal information. Imagine logging into an online banking platform and proving you know your credentials without ever sending them over the network.
This approach not only eliminates the need for transmitting sensitive data but also drastically reduces the risk of credential theft, phishing, and data breaches—offering a more secure and private method of verifying identity.
Secure Voting Systems
In democratic processes, maintaining both voter privacy and election integrity is essential. Zero-knowledge proofs provide a way to verify that each vote is valid and counted correctly, without exposing who voted or how they voted.
In a ZKP-enabled voting system, each voter can prove their vote was cast and included in the final tally, while their individual choices remain entirely confidential. This ensures transparency in the electoral process while safeguarding the core principle of voter anonymity.
Cloud Computing
As more individuals and organizations entrust their data to cloud providers, data integrity and confidentiality have become major concerns. Zero-knowledge proofs offer a powerful solution by enabling users to verify that their data is stored or processed correctly—without having to reveal or download the actual data.
For example, a business could confirm that sensitive financial reports remain untampered in the cloud, or that a computation was performed correctly on private datasets, all without ever exposing the data itself. This strengthens trust between users and cloud providers, supporting secure and privacy-respecting data services.

Challenges and Future of Zero-Knowledge Proofs
While zero-knowledge proofs offer transformative potential in digital privacy and security, their adoption is not without hurdles. As with any emerging technology, ZKPs face technical, practical, and regulatory challenges that must be addressed to unlock their full promise.
Computational Complexity and Performance
One of the most pressing challenges in zero-knowledge proofs lies in their computational overhead. Generating and verifying proofs—especially in complex or large-scale applications—can be resource-intensive. This can lead to delays, increased energy consumption, and scalability issues, particularly in blockchain systems or data-heavy environments.
To address this, ongoing research is focused on developing more efficient proof systems, such as zk-SNARKs and zk-STARKs, which aim to reduce proof size and verification time without compromising security. These innovations are critical to making ZKPs practical for widespread, real-time use across industries.
Understanding and Adoption
Despite their powerful capabilities, zero-knowledge proofs remain conceptually and technically complex, posing a steep learning curve for developers and organizations looking to implement them. Ensuring correct implementation is particularly challenging, as small errors can compromise security or render proofs invalid.
To foster broader adoption, the community must invest in educational resources, development frameworks, and user-friendly tooling. Simplifying integration through standardized libraries and documentation will empower more developers to confidently deploy ZKPs in real-world systems.
Regulatory Considerations
As data privacy laws such as the GDPR, CCPA, and others continue to evolve, zero-knowledge proofs are emerging as a powerful tool for compliance. They offer a way to verify data authenticity and adherence to policies without exposing personal information.
However, integrating ZKPs into existing regulatory frameworks presents unique challenges. Legal standards often require transparency and auditability—concepts that can appear at odds with zero-knowledge approaches. Bridging this gap will require active collaboration between technologists, legal experts, and policymakers to ensure that ZKPs can be used responsibly, ethically, and in alignment with global data governance standards.
The Future of Privacy and Security
ZKPs represent a fundamental shift in how we think about trust, privacy, and verification in the digital age. By enabling individuals and systems to prove the truth of a statement without exposing the underlying data, ZKPs offer a powerful solution to one of the internet’s most persistent dilemmas: how to secure information without surrendering control over it.
As our digital lives continue to expand—encompassing finance, communication, identity, and beyond—the demand for privacy-preserving technologies will only grow. Zero-knowledge proofs are poised to play a central role in this transformation. Whether in secure financial transactions, anonymous voting, or next-generation authentication systems, ZKPs are laying the groundwork for a future where transparency and privacy no longer have to be at odds.
Embracing this technology means more than just adopting new tools—it means reimagining how we design systems, handle data, and establish trust. For developers, businesses, and policymakers alike, understanding zero-knowledge proofs is not only a technical advantage, but a crucial step toward building a safer, more private digital world.




Comments